What's New
Making a big impact while remaining impact-neutral
ACS Omega held its annual Editorial Board meeting on August 13 at the ACS Fall Meeting in San Francisco. Apart from celebrating the many successes over the year, key topics of discussion included journal performance and editorial statistics, active Calls for Papers and future virtual special issue planning, marketing activities, updates on ethical cases, and ongoing and upcoming commissioning plans.
Top image: ACS Omega's achievements since its first article was published in July 2016
New Calls for Papers
Magnetic-based nanohybrids have emerged as a promising solution to some environmental challenges, thanks to their distinctive structure, functionality, and customizable physicochemical properties. These nanohybrids show potential in detecting and treating trace contaminants that conventional alternatives struggle to handle. Our Virtual Special Issue will focus on research on the design, synthesis, characterization, and environmental applications of magnetic nanohybrids. Join us as we explore the exciting possibilities these materials offer in addressing pressing ecological concerns.
Submission Deadline: November 30, 2023
New developments in optoelectronics have been made possible through groundbreaking advancements in novel materials, heterostructures, and innovative device architectures, which have opened up previously untapped possibilities for boosting the efficiency and performance of
optoelectronic devices. Submit your work to our upcoming Virtual Special Issue, which will explore the applications of novel materials in various optoelectronic devices, shedding light on the exciting progress in the field and showcasing the potential for further advancements.
Submission Deadline: April 1, 2024
ACS Omega - In The News
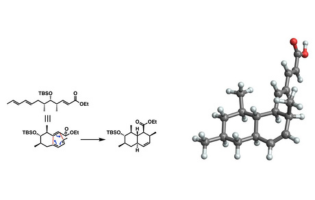
The discovery of antibiotics in 1928 revolutionized medicine, providing a potent tool against bacterial infections. However, overuse led to drug-resistant bacterial strains, posing a global health threat. A research team from Tokyo University of Science achieved a groundbreaking gram-scale synthesis of tanzawaic acid B, a compound with potential for developing new antibiotics, offering hope in the fight against multidrug-resistant bacteria and paving the way for further research into its biological properties and analogs.
Reference: Takatsugu Murata et al., First Total Synthesis of Tanzawaic Acid B, ACS Omega (2023). DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c03634.
The use of functional beverages with the incorporation of lactic acid bacteria has increased considerably in recent years, benefiting a large percentage of the population that is intolerant to dairy products. Considerable attention was given to a study on the effects of heat treatment, specifically pasteurization and sterilization, on a plant-based milk made from coconut and rice. They found that these processes caused the starches in the rice flour to gelatinize and undergo the Maillard reaction. Additionally, the drinks became more acidic and had fewer sugars, potentially impacting their taste.
Reference: Naella Sandivel Valencia Pérez et al, Role of Thermal Process on the Physicochemical and Rheological Properties and Antioxidant Capacity of a New Functional Beverage Based on Coconut Water and Rice Flour, ACS Omega (2023). DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c01761
Journal Metrics
- ACS Omega published 299 articles in July and 421 articles in August 2023.
- ACS Omega's articles were downloaded 1,140,074 times in July and 1,120,797 times in August, a 50.2% increase in usage compared to the equivalent time period in 2022.
Published Issues
Featured Articles
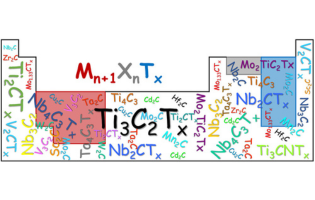
The increasing environmental pollution from industries necessitates the development of effective separation technologies to remove hazardous contaminants, with a focus on using MXene nanomaterials due to their unique properties and excellent separation performance. This review explores the versatility of MXene nanomaterials in various separation applications, emphasizing recent advancements in tuning their separation potential and addressing stability, fouling, regenerability, and swelling concerns in membrane and adsorption-based separation processes.
Şirin Massoumılari and Sadiye Velioǧlu, Gebze Technical University, Türkiye
ACS Omega 2023, 8, 33, 29859–29909
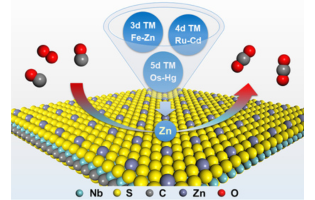
The study examined the potential of 3d, 4d, and 5d transition metal-decorated Nb2S2C monolayers as single-atom catalysts for low-temperature CO oxidation, highlighting that Zn-decorated Nb2S2C is a promising catalyst with a low energy barrier of 0.25 eV. This research suggests that defective carbosulfides could serve as efficient and cost-effective substrates for generating single-atom catalysts for low-temperature CO oxidation.
Yu Jing et al., Nanjing Forestry University, China
ACS Omega 2023, 8, 34, 31051–31059
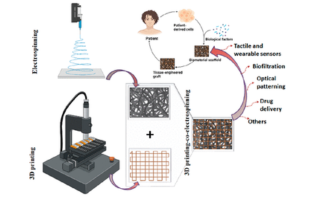
Porous structures in the submicrometer to nanometer size range can be efficiently produced using electrospinning technology, but achieving desired structures can be mechanically challenging. Combining electrospinning with 3D printing offers a versatile method for digitally controlled fabrication of shape-morphing structures, particularly in biomedicine. This integration allows for the creation of advanced materials, including sensors, filtration systems, tissue scaffolds, and optical patterns, with potential applications in the biomedical field, representing a promising avenue for future research and development.
Suprakas Sinha Ray, Dipankar Chattopadhyay et al., University of Calcutta, India and University of Johannesburg, South Africa.
ACS Omega 2023, 8, 31, 28002–28025
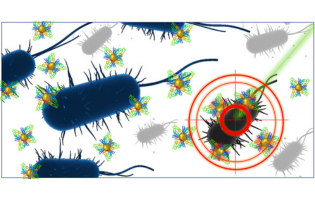
Metal nanoparticles like platinum, silver, and gold have shown promise in inhibiting bacterial growth, but their effectiveness can be influenced by a protein corona formed in biological fluids. This study examined the antimicrobial activity of these nanoparticles, particularly gold, with and without a human serum albumin protein corona against Escherichia coli, revealing that the protein corona can modulate their antimicrobial effects, suggesting potential for innovative approaches to combat antibiotic resistance.
Alexa Guglielmelli, Giovanna Palermo et al. University of Calabria and CNR-NANOTEC, Institute of Nanotechnology, Italy.
ACS Omega 2023, 8, 34, 31333–31343
The study explores recycling lithium-ion batteries and focuses on improving the recycling of active electrode materials. It finds that a dielectrophoretic high-throughput filter can effectively separate lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) from graphite particles, offering a promising method for obtaining nearly pure LiFePO4 fractions from mixed materials.
Georg R. Pesch et. al, University College Dublin, Ireland & University of Bremen, Germany
ACS Omega 2023, 8, 29, 26635–26643
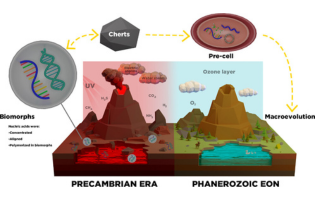
In this work, the hypothesis based on the condition that silica-carbonates of alkaline earth metals, called biomorphs, are the ones that could unify all the proposed theories on the origin of life is proposed. Aimed at evaluating if this hypothesis is viable, this work assessed whether biomorphs are able to protect the DNA from continuous UV radiation under two conditions that emulate the habitats that could have co-existed in the Precambrian and, after the radiation, evaluated the time during which DNA remained inside the biomorphs.
Mayra Cuéllar-Cruz, Universidad de Guanajuato, Mexico
ACS Omega 2023, 8, 32, 29585–29594
Why are chemistry articles retracted? The answer to this and a more in-depth analysis of retractions are covered in this interesting viewpoint.
Yulia Sevryugina, University of Michigan Library, United States
ACS Omega 2023, 8, 35, 31568–31574
Previous Newsletters
Click below to view a previous ACS Omega Monthly Update:
© 2025 American Chemical Society, 1155 16th St NW, Washington, DC 20036, USA. View our Privacy Policy