What's New
2021 Wilhelm Exner Medal Laureates Prof. Katalin Karikó (left) and Prof. Luisa Torsi (right). Credits Lena Horvath and the Wilhelm Exner Medal Foundation.
We are extremely proud to announce that our Associate Editor, Professor Luisa Torsi, was presented with her 2021 Wilhelm Exner Medal this month by Federal Minister Leonore Gewessler in a ceremony at the Palais Eschenbach in Vienna, Austria. The medal is awarded by the Austrian Craft and Trade Association to honor scientists who's findings have led to or initiated important applications in the fields of trade or industry, and Professor Torsi received the award for her pioneering research in the field of organic bioelectronics.
Many congratulations again to Luisa on behalf of all of us at ACS Omega.
Key Journal Metrics
- ACS Omega published 347 articles in the month of May, for a total of 1,704 YTD. As compared to the equivalent timeframe in 2021, this represents a 27.4% increase in published output.
- Articles published by ACS Omega were downloaded 725,725 times in May, which represents a 19.6% increase in usage compared to the equivalent time period in 2021.
Published Issues
pp. 14402-15257
pp. 15258-16235
pp. 16236-16846
pp. 16847-17501
Featured Articles
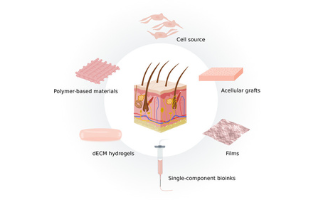
In our latest ACS Editors' Choice selection, the authors review recent developments in tissue bioprinting, cellularized bioink formulation, and cell tracking, from both chemistry and cell biology perspectives. A general conclusion is reached that in order to drive further advancements in this field toward clinical application, a highly interdisciplinary approach including a broad range of scientific expertise such as polymer science, nanoscience, and cell biology/tissue engineering is required.
Luis M. Liz-Marzán*, Ander Izeta* et al CIC biomaGUNE and Biodonostia Health Research Institute, Spain
ACS Omega 2022, 7, 19, 16236–16243
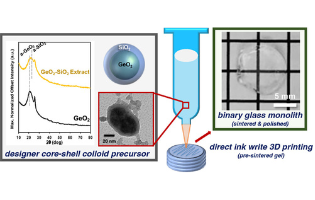
In this article, the authors report the design and use of core–shell germania–silica (GeO2–SiO2) colloids and their use as precursors to fabricate GeO2–SiO2 glass monoliths by direct ink write (DIW) 3D printing. Characterization of the glass components demonstrates that the core–shell GeO2–SiO2 presents a feasible route to prepare quality, optically transparent low wt % GeO2–SiO2 glasses by DIW printing. Additionally, the results offer a novel, hybrid colloid approach to fabricating 3D-printed Ge-doped silica glass.
Joel F. Destino* et al Creighton University and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, United States
ACS Omega 2022, 7, 20, 17492–17500
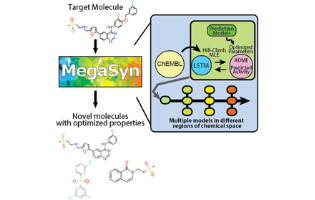
In this article, the authors introduce a suite of automated tools called MegaSyn representing three components: a new hill-climb algorithm, which makes use of SMILES-based recurrent neural network (RNN) generative models, analog generation software, and retrosynthetic analysis coupled with fragment analysis to score molecules for their synthetic feasibility. They demonstrate that by deconstructing the targeted molecules and focusing on substructures, combined with an ensemble of generative models, the tools generally perform well for generating new scaffolds as well as targeted analogs, which are likely synthesizable and druglike. Further, the development, benchmarking, and testing of this suite of tools is described, and the potential uses to optimize molecules or prioritize promising lead compounds proposed.
Sean Ekins* et al. Collaborations Pharmaceuticals, Inc and Workflow Informatics Corporation, United States
ACS Omega 2022 (ASAP)
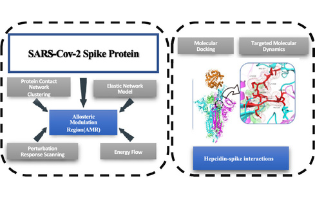
In this article, the authors present a multifaceted computational approach strongly grounded on a biophysical modeling of biological systems, so to disclose the interaction of the SARS-CoV2 spike protein with ACE2 with a special focus to an allosteric regulation of the spike–ACE2 interaction. The correspondence between hinge sites and the Allosteric Modulation Region (AMR) in the S-ACE complex suggests a molecular basis for hepcidin involvement in COVID19 pathogenesis. The importance of AMR in different states of spike is verified and its interactions with HPC and the consequence of the HPC-AMR interaction on spike dynamics and its affinity for ACE2 are studied. Two complementary mechanisms for HPC effects on spike of SARS-CoV-2 are proposed, though is stressed that clear molecular in vivo verification beside clinical observations are needed.
Luisa Di Paola*, Guang Hu* et al. Università Campus Bio-Medico di Roma, Italy and Soochow University, China
ACS Omega 2022, 7, 20, 17024–17042
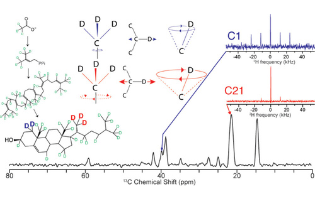
The authors present a cost-effective means of 2H and 13C enrichment of cholesterol. This method exploits the metabolism of 2H,13C-acetate into acetyl-CoA, the first substrate in the mevalonate pathway. They show that growing the cholesterol producing strain RH6827 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in 2H,13C-acetate-enriched minimal media produces a skip-labeled pattern of deuteration. The cholesterol labeling pattern is characterized by mass spectrometry and solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. This result establishes that this cholesterol labeling pattern will have great utility in reporting on cholesterol dynamics and orientation in a variety of environments and with different membrane bilayer components, as well as monitoring the mevalonate pathway product interactions within the bilayer. The work also demonstrates the flexibility and universality of acetate labeling.
Benjamin J. Wylie* et al. Texas Tech University, United States
ACS Omega 2022, 7, 20, 17151–17160
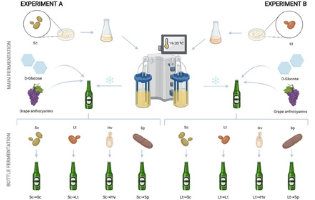
In recent years, the interest in craft beers has increased considerably due to the demand for new beverages and the consumer’s willingness to pay higher prices. This article explores the sensorial changes produced in craft beers by using different Saccharomyces and non-Saccharomyces yeasts with several instrumental and sensory analyses performed. Of note is the increased production of aromatic esters, including 2-phenylethyl acetate in the H. vineae conditioning, which is associated with a high aromatic quality, as well as ethyl lactate in all samples, whose main fermentation was carried out with L. thermotolerans. Although this research is at an early stage, future complementary studies may shed more light on this topic.
Cristian Vaquero* et al. Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, Spain
ACS Omega 2022, 7, 21, 17822–17840
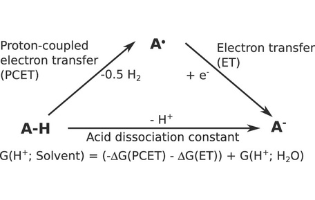
Most of the pKa values reported in the literature refer to the acid dissociation in an aqueous medium. In this work, the authors describe a simple, robust and yet truly general theoretical procedure that may be used to estimate the pKa of any compound in any solvent. Given the experimental difficulties in assessing the pKa of compounds in non-aqueous media, and the critical value of Acid–base properties of molecules to almost all areas of chemistry, the methodology described in the article is a very valuable and timely advance in the field.
Michael Busch* et al. Aalto University, Finland, Uppsala University, and University of Gothenburg, Sweden
ACS Omega 2022, 7, 20, 17369–17383
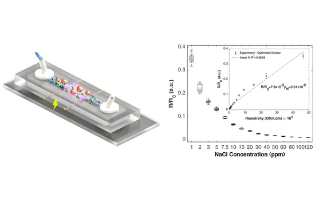
Rapid, inexpensive, and precise water salinity testing remains indispensable in water quality monitoring applications. Despite the plethora of sensors and commercialized devices to monitor seawater salinity, salt detection and quantification at very low levels of drinking water (below 120 ppm) have often been overlooked. In this paper, the authors report on optimization of a low-cost microfluidic sensor to measure water salinity in the range of 1–120 ppm. The proposed design employs two copper microbridge wires suspended orthogonally in a PDMS microchannel to measure salinity based on the electrical resistance between the wires. There is future potential for this sensor to be integrated into a hand-held device to remove present impediments for low-cost and ubiquitous salinity surveillance of drinking water.
Nima Tabatabaei*, Pouya Rezai* et al. York University, Canada
ACS Omega 2022, 7, 18, 15529–15539
Previous Newsletters
Click below to view a previous ACS Omega Monthly Update
© 2025 American Chemical Society, 1155 16th St NW, Washington, DC 20036, USA. View our Privacy Policy